Asexual Versus Sexual Reproduction
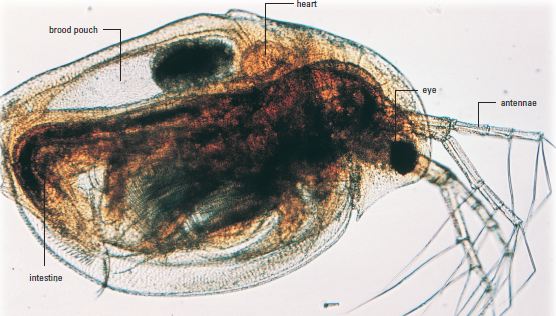
Life on Earth can only sustain because of a species ability to reproduce. Reproduction is the mechanism to which species are able to continue surviving on this planet from generation to generation. The mechanism of reproduction can occur both asexually and sexually. Asexual Reproduction is the production of offspring from a single parent. These offspring inherit the genes of that parent only and are genetic copies of their parent. Sexual Reproduction is the production of offspring from the union of two sex cells, one from each different parent. The genetic makeup of the offspring is different from that of either parent. When the two sex cells come into contact, fertilization occurs. This is the union of female and male sex cells (e.g. ovum and sperm in humans). Daphnia (a crustacean), also known as a water flea, is studied quite frequently by scientists because it is capable of reproducing both asexually and sexually.
Principles of Cell Division
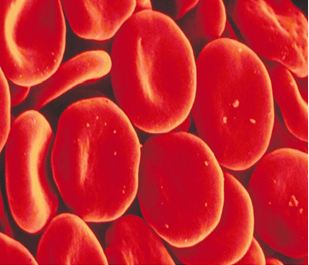
Starting from a single fertilized egg, the human body is composed of approximately 100 trillion cells! That is a lot of cell division that occurs without us even noticing. Cell theory states that all living things, like humans, are made up of one or more cells which are all formed pre-existing cells through cell division. Tissue growth and maintaining a fully grown individual require cell division. For example, a normal person contains about 25 trillion red blood cells, yet the life span of a red blood cell is only 20 to 120 days. Cell division is required in order to replenish the red blood cells that have died off.
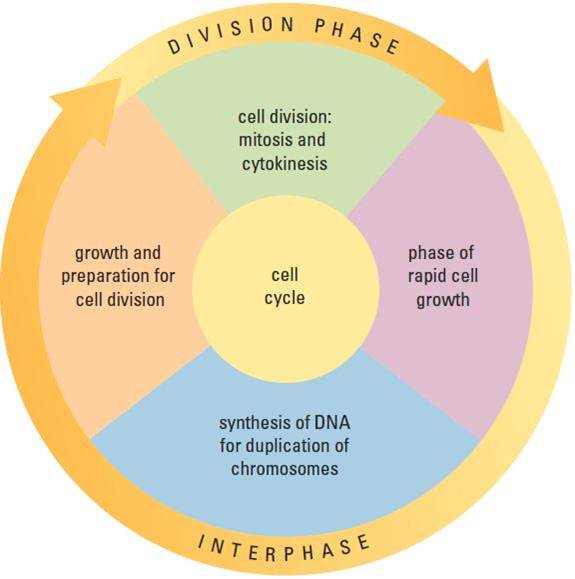
Interphase
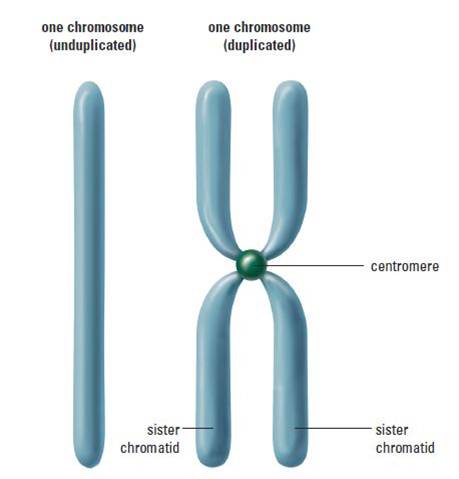
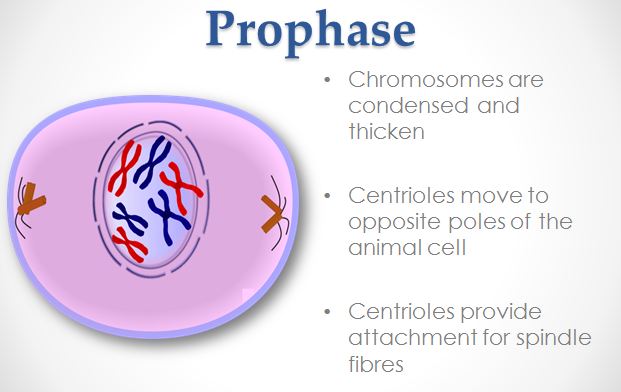
Students and even teachers often confuse interphase as being part of mitosis. This is a misconception. Interphase is the time interval between nuclear divisions. During this phase, a cell increases in mass, roughly doubles the cytoplasmic components, and duplicates its chromosomes. During Interphase, the genetic material is called chromatin and includes all the DNA molecules and associated proteins in the nucleus. Each chromosome duplicates itself during interphase and is attached by centromeres. The chromosomes are called sister chromatids at this time.
Mitosis
Here is great simulation of Mitosis: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VlN7K1-9QB0
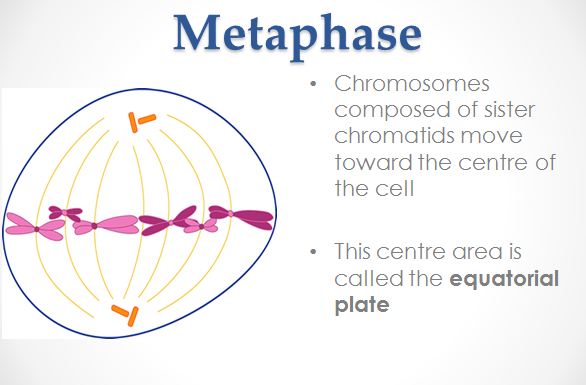
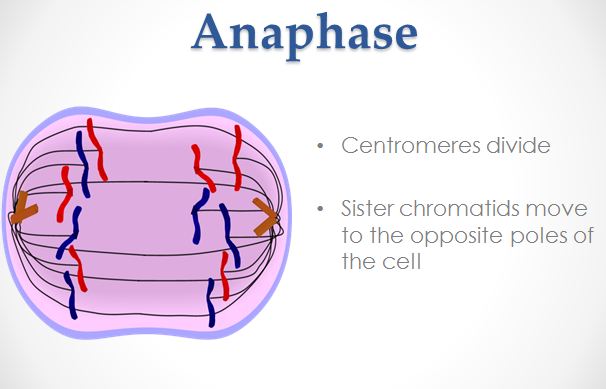
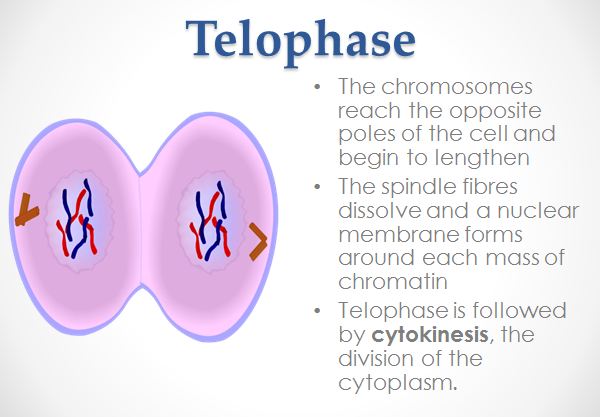
Mitosis is a type of cell division in which a daughter cell receives the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It should be noted that cells that undergo mitosis such as the tissues of the body that exclude sex cells are called somatic cells. During mitosis, the cytoplasm with divide into two cells and this is called cytokinesis. The phases of mitosis are as follows:
To summarize: